Webpack Wordpress
This webpack plugin serves two purposes:
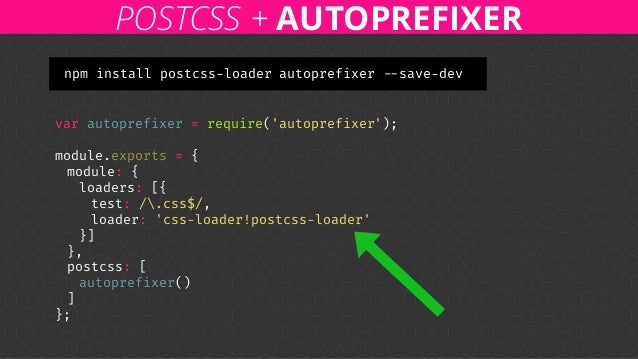
WebPack Backstage is a WordPress Speed Optimization & Security Service that keeps your website running at top speeds by fixing all of the hidden technical problems that are gumming up the works. Poor security can cause a lot of problems for your WordPress website. It leaves all of your data vulnerable to exploitation by hackers. Webpack comes with it’s own auto-reloading devServer, but it’s difficult to get it working with WordPress. So instead, we’ll utilize the BrowserSync plugin to handle reloading our browser every time we make a change. As before, our first step is to require the BrowserSyncPlugin. Webpack for WordPress, Part 1: Adding Webpack to your WordPress theme This tutorial will walk you through the basics of how to add webpack to your next WordPress theme and customize the config. Ian.pvd 1985 – 2018.
- Externalize dependencies that are available as script dependencies on modern WordPress sites.
- Add an asset file for each entry point that declares an object with the list of WordPress script dependencies for the entry point. The asset file also contains the current version calculated for the current source code.
This allows JavaScript bundles produced by webpack to leverage WordPress style dependency sharing without an error-prone process of manually maintaining a dependency list.
Consult the webpack website for additional information on webpack concepts.
Installation Installation
Install the module
Note: This package requires Node.js 12.0.0 or later. It also requires webpack 4.8.3 and newer. It is not compatible with older versions.
Usage Usage
Webpack Webpack
Use this plugin as you would other webpack plugins:
Note: Multiple instances of the plugin are not supported and may produced unexpected results. If you plan to extend the webpack configuration from @wordpress/scripts with your own DependencyExtractionWebpackPlugin, be sure to remove the default instance of the plugin:
Each entry point in the webpack bundle will include an asset file that declares the WordPress script dependencies that should be enqueued. Such file also contains the unique version hash calculated based on the file content.
For example:
By default, the following module requests are handled:
| Request | Global | Script handle |
|---|---|---|
@babel/runtime/regenerator | regeneratorRuntime | wp-polyfill |
@wordpress/* | wp['*'] | wp-* |
jquery | jQuery | jquery |
lodash-es | lodash | lodash |
lodash | lodash | lodash |
moment | moment | moment |
react-dom | ReactDOM | react-dom |
react | React | react |
Note: This plugin overlaps with the functionality provided by webpack externals. This plugin is intended to extract script handles from bundle compilation so that a list of script dependencies does not need to be manually maintained. If you don’t need to extract a list of script dependencies, use the externals option directly.
This plugin is compatible with externals, but they may conflict. For example, adding { externals: { '@wordpress/blob': 'wp.blob' } } to webpack configuration will effectively hide the @wordpress/blob module from the plugin and it will not be included in dependency lists.
Options Options
An object can be passed to the constructor to customize the behavior, for example:
outputFormat
- Type: string
- Default:
php
The output format for the generated asset file. There are two options available: ‘php’ or ‘json’.
combineAssets
- Type: boolean
- Default:
false
By default, one asset file is created for each entry point. When this flag is set to true, all information about assets is combined into a single assets.(json|php) file generated in the output directory.
combinedOutputFile
- Type: string
- Default:
null
Webpack Wordpress Sass
This option is useful only when the combineAssets option is enabled. It allows providing a custom output file for the generated single assets file. It’s possible to provide a path that is relative to the output directory.
useDefaults
- Type: boolean
- Default:
true
Pass useDefaults: false to disable the default request handling.
injectPolyfill
- Type: boolean
- Default:
false
Force wp-polyfill to be included in each entry point’s dependency list. This would be the same as adding import '@wordpress/polyfill'; to each entry point.
requestToExternal
- Type: function
requestToExternal allows the module handling to be customized. The function should accept a module request string and may return a string representing the global variable to use. An array of strings may be used to access globals via an object path, e.g. wp.i18n may be represented as [ 'wp', 'i18n' ].
requestToExternal provided via configuration has precedence over default external handling. Unhandled requests will be handled by the default unless useDefaults is set to false.
requestToHandle
- Type: function
All of the external modules handled by the plugin are expected to be WordPress script dependencies
and will be added to the dependency list. requestToHandle allows the script handle included in the dependency list to be customized.
If no string is returned, the script handle is assumed to be the same as the request.
requestToHandle provided via configuration has precedence over the defaults. Unhandled requests will be handled by the default unless useDefaults is set to false.
requestToExternal and requestToHandle
The functions requestToExternal and requestToHandle allow this module to handle arbitrary modules.
requestToExternal is necessary to handle any module and maps a module request to a global name.
Webpack Wordpress Boilerplate
requestToHandle maps the same module request to a script handle, the strings that will be included in the entrypoint.asset.php files.
WordPress WordPress
Webpack Wordpress
Enqueue your script as usual and read the script dependencies dynamically:
